In this article, we analyze the sport of rhythmic gymnastic in physical education. How can we work on it? What benefits does rhythmic gymnastics bring to our PE area?
What is rhythmic gymnastic?
Before analyzing what rhythmic gymnastic in physical education is, it is important to note that it consists of 6 modalities: Artistic, Rhythmic, Trampoline, Aerobic, Acrobatic, and General. Next, we will focus on defining what rhythmic gymnastics is.
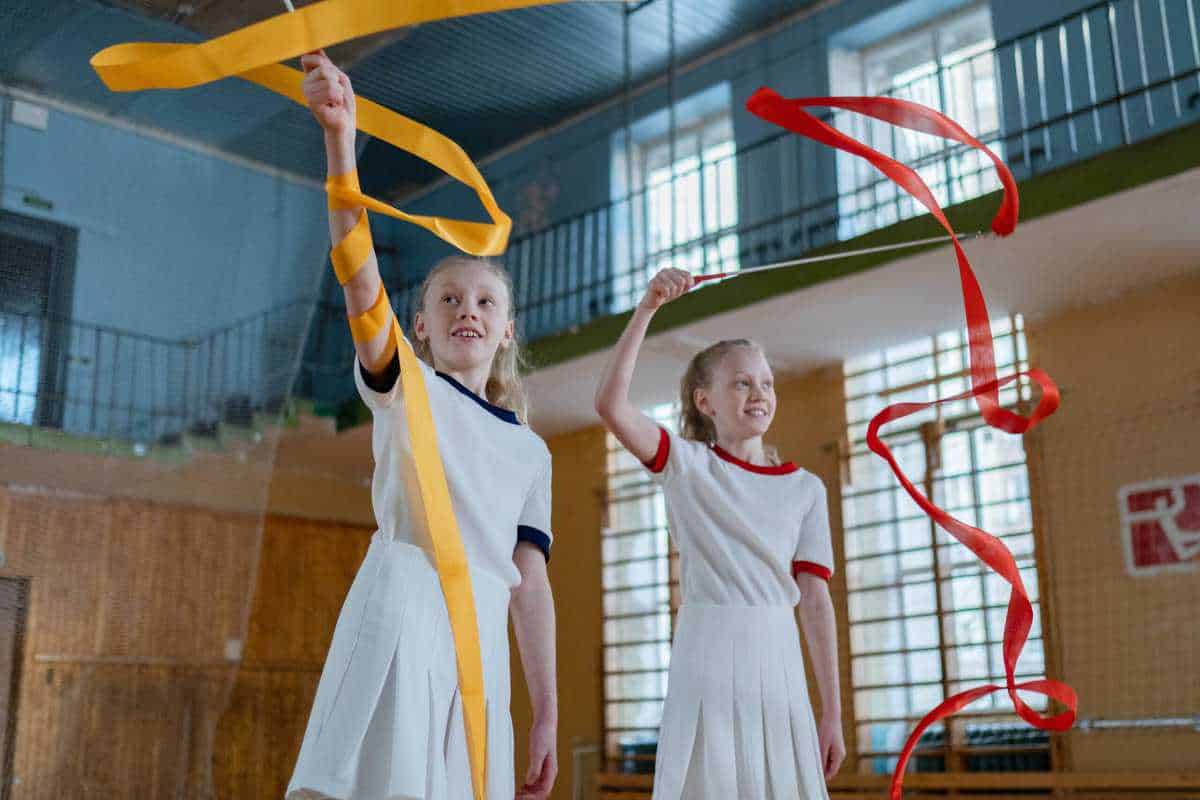
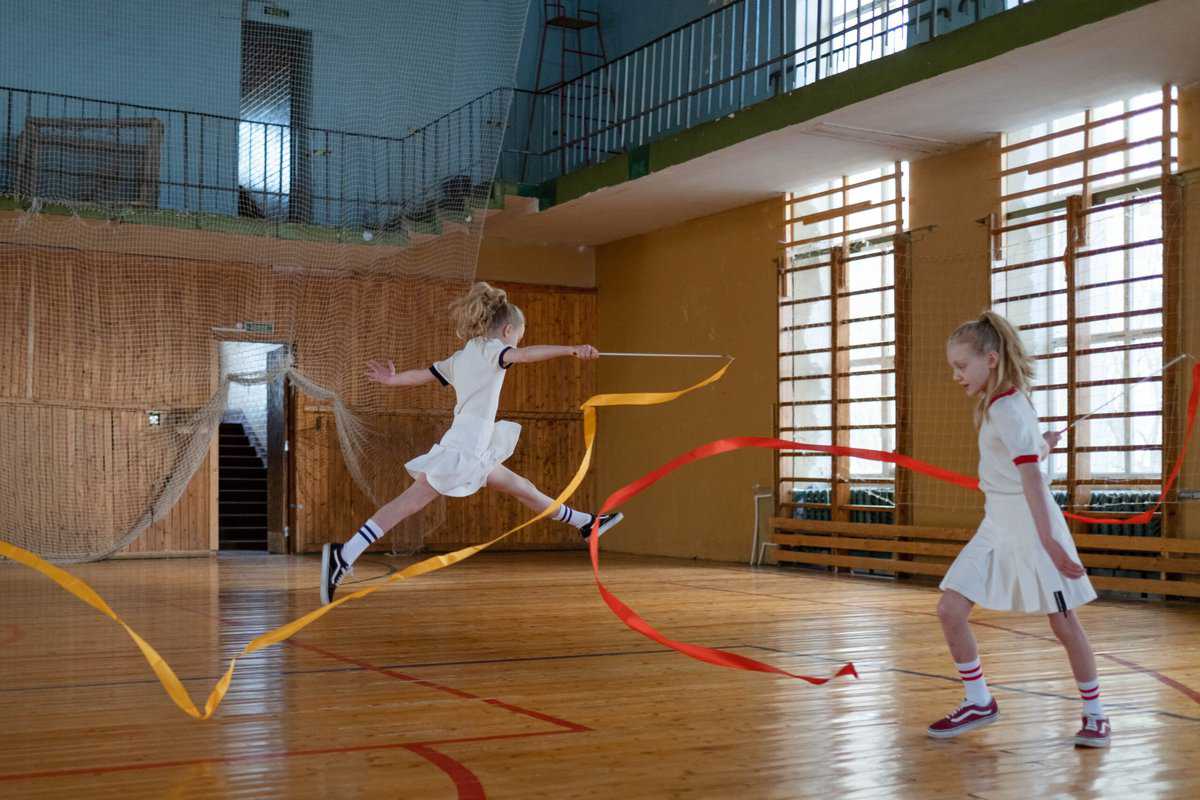
Rhythmic gymnastics is a specialization of traditional gymnastics, which is a female practice that uses background music and certain materials with different types of mobile apparatuses, performing various exercises and free evolutions, showcasing flexibility, elegance, and body control.
Therefore, as a result, we can observe that proprioception and body control merge to the rhythm of the music, leading to the development of choreographic sequences.
As a result, in this discipline, the youngest gymnasts will learn to shape their bodies as they gain the skill and technique required.
In the area of physical education, rhythmic gymnastics in physical education means that the objectives are different from those in the competitive area, that is, we are not going to focus on training a gymnast, but rather we will work on rhythmic gymnastics as a resource within a content block so that they learn to be competent based on the curriculum objectives.
Therefore, it can be used to improve body expression, as a sport mixed with games, etc. But the purpose in school sports is based on learning within the school framework.
Brief historical contextualization about rhythmic gymnastics
Meirone-Matus, & Reyno-Freundt (2022) highlight that the origin of rhythmic gymnastics is practically the same as that of artistic gymnastics because rhythmic gymnastics has remained in the shadow of artistic gymnastics. Thus, we can see that it has its roots in ancient Greece, where it was practiced in physical education.
Gymnastics has evolved over time, and its meaning has evolved and changed. For example, in Greece, gymnasts were prepared for the Olympic Games, and in Rome, initially, gymnastics had a militaristic purpose. That is, the purpose of gymnastics was preparation for war.
But, over time, Emile Jacques Dalcroze followed in the footsteps of his predecessors by adding music and rhythm. Over time, there were three authors named Rudolf von Laban, Wigman Marie, and Medau Henrich who continued working to improve this sport, which in the early 1920s came to be called modern gymnastics.
Therefore, it is suspected that it was born as a variant of modern dance and classical ballet, and it was in Tallinn where the first championships were held in 1947. This sport evolved very quickly until in 1962, the International Gymnastics Federation recognized rhythmic gymnastics as an official discipline.
In 1964, the first world championship was held, and it was not until the 1973 championship that gymnasts from the United States could participate, and it was from there that it began to gain independence as a sports modality.
Individual rhythmic gymnastic was introduced in the Los Angeles Olympics of 1984 and the Atlanta Olympics of 1986. This has contributed to gymnasts having to develop increasingly complex routines because there is more competitiveness, which requires them to be more expressive.
Characteristics of rhythmic gymnastics in physical education
In rhythmic gymnastics in physical education, we can find characteristics of different types, technical, regulatory, attitudinal, etc.
In rhythmic gymnastics in physical education, the most important are the technical components of this discipline, which is composed of body elements that must be mastered just as before practicing competitive swimming, basic aquatic skills must be assimilated.
Therefore, in gymnastics, they are highlighted in two major groups, in the fundamental groups appear jumps, balances, turns, flexibility, and other groups such as displacements, jumps, swings, and circumductions and turns.
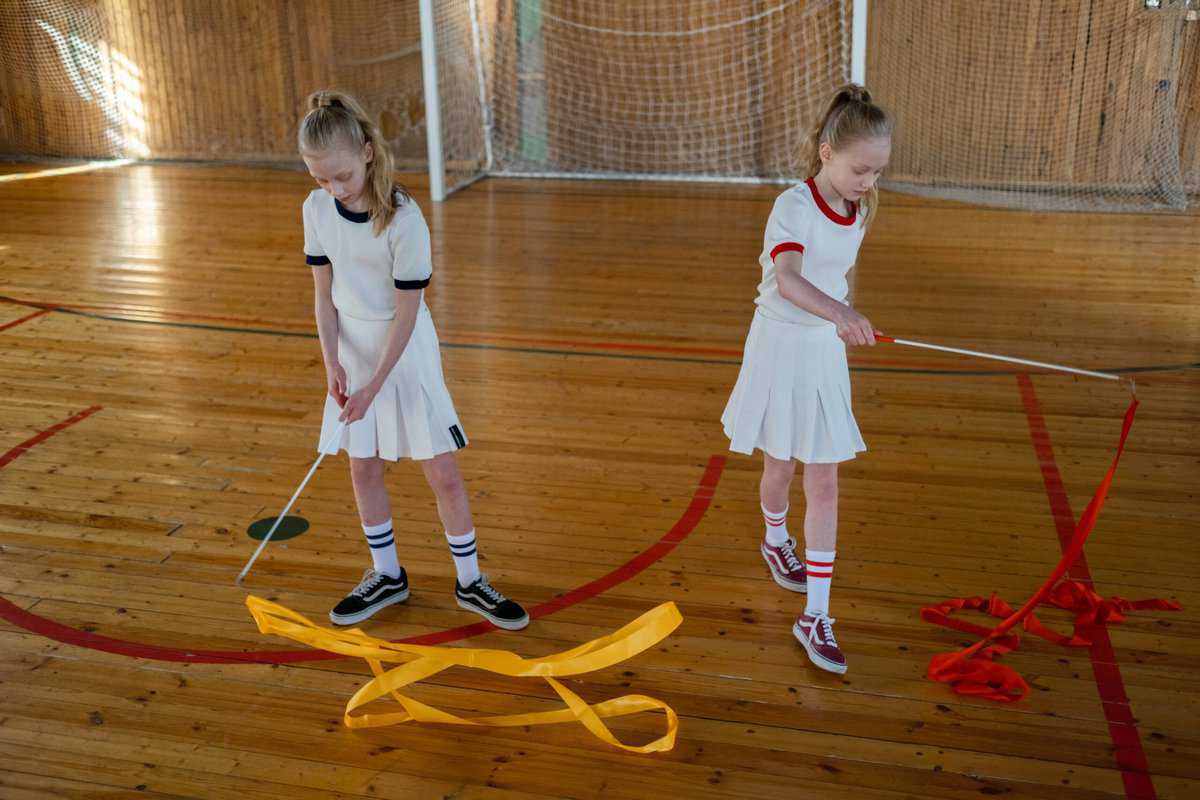
On the other hand, this peculiar discipline is composed of different apparatuses that require specific body elements and techniques, among which we can highlight the rope, hoop, ball, club, and ribbon. Also, the physical preparation required for this discipline is very important, as it is based on the development of conditional and coordinative qualities.
In rhythmic gymnastics in physical education, at the regulatory level, the component of the rules that they have to learn and carry out in competitions, which is regulated by the federation, and they have to learn all the rules of the game to apply them in competition.
Benefits of rhythmic gymnastic in physical education
In rhythmic gymnastic in physical education, we can find multiple benefits from the effect that gymnastics has on children:
- Connects children and athletes with living in the moment, because it is a discipline that makes them aware of their body and the movements they have to perform. Therefore, gymnastics helps correct body elements and improves balance.
- It also helps with the expression of emotions.
- It enhances environmental perception, spatial orientation, and increases reaction speed.
- Improves physical condition and flexibility.
- Exercises the mind through concentration work.
- Stimulates coordination, aesthetics, and group work.
Methodology to be followed by the physical education teacher for designing a rhythmic gymnastic in physical education proposal
In rhythmic gymnastics in physical education, that is, in physical education, the methodology that the teacher must follow will consist of using new learning tools to attract students to new learning experiences. Therefore, active methodologies will be used.
Practical examples for the proposal of rhythmic gymnastic in physical education
In rhythmic gymnastics in physical education, different practical proposals will be suggested to work with secondary school students:
- The warm-up: In which the body is prepared for the main part of the same session. It will consist of two parts. A general one in which the CNS is excited, and metabolism and body temperature are increased, using the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
Finally, the more specific part adapts the physical work in the motor system to favor the development of muscular activity, according to the main part to be performed.
It is proposed that they learn gymnastic skills: Three main gymnastic skills are proposed:
Forward roll: It is proposed that from a squatting position with arms extended forward, they push forward by extending the legs, supporting the arms on the mat, bringing the leg to the chest, looking at the navel, and keeping the hips high. Then the knees are bent, accompanying the movement with the trunk until reaching the initial position. This movement ends standing up.
Backward roll: It starts in a squatting position, facing the opposite direction of the movement, with hands at head height and palms facing up, the performer pushes backward, rolling over the back and supporting hands on the floor, which in turn will serve to push again and finish the movement standing up.
Inverted candle position: The performer prepares in a supine position, making a push that brings the extended legs upwards using the arms on the floor as a stability tool. The position consists of maintaining this posture for a few seconds, applying great isometric force through the abdominals.
- In rhythmic gymnastics in physical education, the Corza exercise: It will consist of a displacement in the sagittal plane, in which a jump is made as the initial position, and then in the air, 4 counts are performed, where the first two counts are of flight, and the legs are raised to the maximum, and the last two counts are of landing.
- In rhythmic gymnastics in physical education, the fourth exercise: It consists of doing the backward roll with the back rounded backward and arms stretched upwards, rotating backward, and ending the exercise with a flexion. In contrast, the fifth is the same as the fourth, but the last arm support allows leaving the ground to the normal position, using the push of the arms.
Bibliographic references
- Pamela Echeverría-Caranqui, J. I., Omar León-Jácome, G. I., & Leonidas Puga-Burgasi III, G. (2021). Methodological Analysis of the Teaching-Learning Process of Rhythmic Gymnastics for Physical Education Teachers, 6(08), 1012–1027. https://doi.org/10.23857/pc.v6i8.2996
- Meirone-Matus, N., & Reyno-Freundt, A. (2022). Rhythmic gymnastics in school vs. gender identity, 75, 28–36. Retrieved from http://emasf.webcindario.com/La_gimnasia_ritmica_en_la_escuela_versus_identidad_de_genero.pdf
- Garrido, A. L. (1990). Rhythmic sports gymnastics: A “Sport” in school age. Retrieved from https://es.slideshare.net/anguepla/la-gimnasia-pedaggica