We analyze postural education. The term posture refers to the position our body adopts in the usual situations of our life. When we are standing, sitting, lying down, or engaging in physical activity, our body adopts different postures.
Numerous factors influence body posture, such as fatigue, muscle tone, heredity, incorrect positions we adopt, emotions themselves… Additionally, through our posture, we can establish non-verbal communication, for example: low self-esteem or a very introverted person is associated with keeping the head down (1).
Our spine constitutes a fundamental structure of our body and as we have already seen in other articles from MundoEntrenamiento, it is a true engineering masterpiece. It has great resistance, but despite this, it is subjected daily to numerous pressures and tensions that negatively affect our health. Therefore, we must take care of it and try to maintain proper postural education in our daily lives.
What does postural education mean?
Postural education is a set of techniques and exercises designed to improve the posture of the human body. Postural education focuses on teaching people how to maintain correct and healthy posture while performing their daily activities.
Postural education can include stretching, strengthening, and relaxation exercises, as well as breathing and body awareness techniques.
The goal of postural education is to reduce pain, prevent injuries, and improve the overall health of the person. Postural education is especially important for those who spend long hours sitting or standing, such as office workers, drivers, students, etc.
Incorrect posture can cause tension and stress in the muscles, bones, and joints, which can lead to long-term pain and injuries. Postural education helps prevent these problems and maintain a healthy and strong body.
Common pathologies related to the spine
Hyperlordosis: This is a very exaggerated increase in the curvature of the lumbar area, with anterior convexity.
Kyphosis: this pathology is an exaggeration of the dorsal curvature.
Scoliosis: this pathology consists of a deviation of the spine, with reference to a median longitudinal axis of the torso area. It is characterized by excessive stiffness of the spine (2).
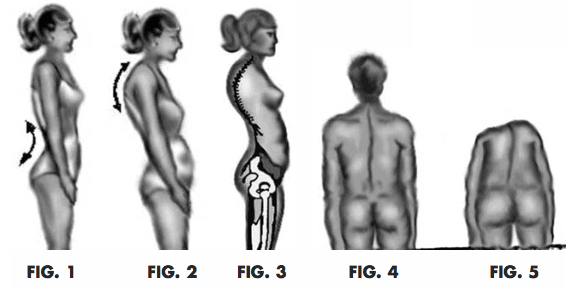
If we really want to prevent these and other pathologies related to back pain, we must take into account a series of simple considerations.
Upright position
When standing, we should not slouch, we must avoid letting the shoulders fall forward as this can enhance and cause the development of hyperkyphosis. Our head should remain straight without inclinations and the pelvis should be stable (2).
Sitting position
In the sitting posture, our trunk should be upright, with our lumbar and dorsal areas well attached to the backrest of the seat, always avoiding letting our neck fall down, as this will directly result in excessive tension on the cervical area.
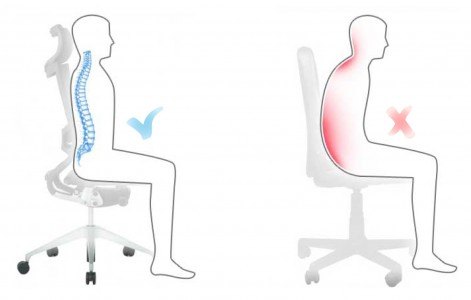
Lying posture
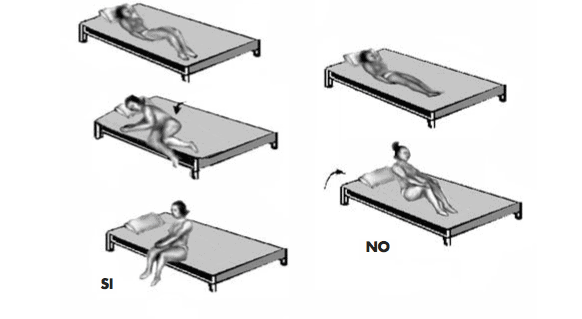
A large part of our life is spent sleeping, so the posture in bed is essential to maintain correct spinal health.
The mattress should be firm and straight, but not excessively hard, as this can be as harmful as being too soft. Our pillow should not be very thick to avoid misalignment of the head with respect to the spine.
Regarding postures, one of the most recommended is the fetal position. In this posture, with the hips and knees flexed, the spine is completely unloaded, free of pressures.
Another important aspect is when getting out of bed, first, we should turn to the side and then, with the help of the arm in contact with the mattress, get up completely. It is not advisable to get up abruptly (3, 4, 5).
Postures in daily activities
Throughout our lives, we perform countless movements that must be done properly, otherwise, they can significantly affect our spine.
To avoid problems, we will leave you a series of practical tips to carry out in your daily life.
Lifting and handling objects
When lifting an object, the first thing we must do is bring it close to our center of gravity and then grab it with our legs and hips flexed, the trunk upright, and ascend by extending the lower body.
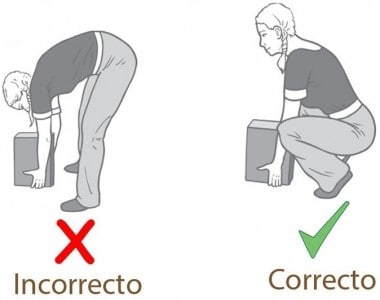
Personal hygiene
If our sink is excessively low, when shaving, brushing our teeth, etc., we must bend excessively, and this is completely discouraged as we are forcing a hyperkyphotic position. To avoid this, it is recommended to keep the spine as straight as possible.
Typing on the computer
The position when using our PC is essential to maintain a healthy back and avoid subsequent pathologies. We must maintain an aligned posture, with 90 degrees in knees and hips, and our gaze directed directly at the screen without our head tilting excessively, thus avoiding unnecessary cervical tension (3).

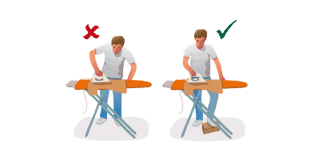
Ironing
If possible, it is recommended to perform this household activity sitting down. Another option is to place a footrest, alternating the support foot on it, to relieve pressure on the lumbar area.
Going shopping
When we go to the supermarket, we must distribute the weight of the bags evenly in both hands. Although the most advisable is to use a wheeled cart and push it from the front with both arms.
Vacuuming
We should always use the vacuum cleaner’s long tube whenever possible to maintain an upright position. Additionally, we will step one leg forward over the other, in semi-flexion. When vacuuming under the bed or furniture, we will flex the hips and knees instead of the spine.
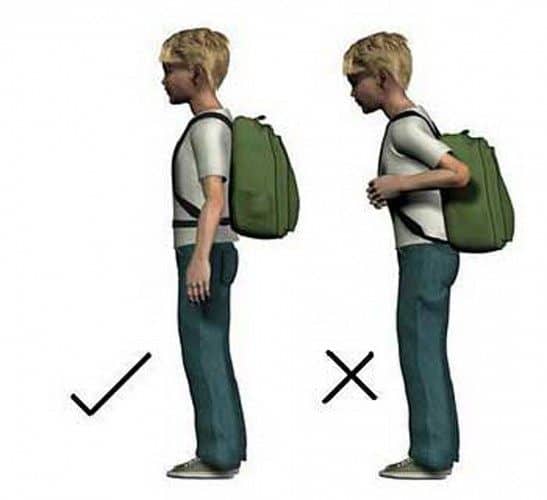
Backpacks
We must avoid carrying unnecessary weights, but if using a backpack, we should place it in the upper area. This way, we will reduce tensions in our lumbar area (3).
Prevention exercises
We can prevent many back problems by performing mobility and strengthening or relaxation exercises.
The cat: in a quadruped position, curve the back and lower the head, then raise the head and gently arch the back (1).

Mobilize the back: lying on your back, flex your knees and lift them, turning the trunk until bringing the knees to one side of your body.
Relieve tension in the back: lying on your back, flex your legs and support the palms of your hands on the floor and your forearms. As you inhale, lift the hips and then the middle of the back without making any arch. Hold the posture for a couple of seconds and return to the initial position (1).

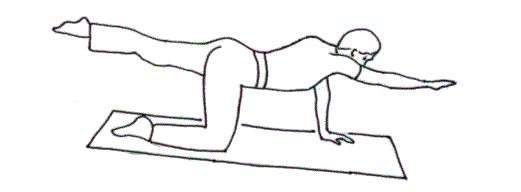
Asymmetric exercise: on your knees, raise the opposite arm and leg only until the leg forms a straight line with the body.
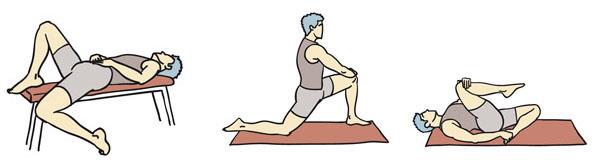
Relax the back: lie down and flex your hips and knees, resting your legs on a chair or flat surface. Hold this position for a few minutes while breathing gently.
Roll on the back: rolling on the back on a mat or soft surface, we can perform a gentle self-massage on the back muscles (1).

Psoas stretch: the psoas is a muscle that, when shortened, can cause excessive tension in the lumbar vertebrae, resulting in annoying pain in the lower back.
How to develop postural education?
Postural education refers to the adoption of habits and techniques to maintain correct and healthy body posture. Here are some steps that can help develop good postural education:
- Body awareness: The first step to good posture is becoming aware of your body and how you feel. Take a moment to assess how you are sitting, standing, or walking and ensure your body is in a neutral position.
- Strengthening and flexibility exercises: Exercises that help strengthen and flex key muscles in your body can improve your posture. Consider practicing exercises like yoga or pilates, which focus on body alignment and posture.
- Ergonomics: Evaluate your workplace and make the necessary adjustments to ensure proper posture while working. Make sure your chair and desk are at the right height and that your screen is at eye level.
- Regular breaks: Taking regular breaks to stretch and walk a bit can help prevent muscle fatigue and tension in the body.
- Attention to feet: Ensure your feet are supported on the floor while sitting and aligned with your knees and hips. Wear comfortable shoes and avoid high heels.
- Postural correction: If you have posture problems, consider working with a physical therapist or personal trainer to correct muscle imbalances and improve your posture.
Remember that postural education is an ongoing process and requires constant practice. Over time, you will adopt healthy habits that will improve your posture and reduce the likelihood of pain and injuries in the future.
Bibliography
- Castro Blanco, F. J. (2008). Postural education. Theory and practice. Revista Digital, Buenos Aires. 12(17).
- Pazos, JM, Aragunde, JL (2000). Postural education. Barcelona: INDE.
- Medina Jiménez, E. (2003). Physical activity and integral health. Barcelona: Paidotribo.
- Fredes, M. Mairlot, MB (2000). Masters and keys of posture. Barcelona: Paidotribo.
- Gattoronchieri, V. (2005). The correct posture. Barcelona: De Vechhi.

