This article aims to briefly explain the importance of strength training, all focusing on eccentric contractions and therefore eccentric regime training. In addition to providing information on the muscle brace.
Strength training
Strength is an essential component for the performance of any person and athlete (8). Thus, a low level of muscle strength, and consequently muscle weakness, is one of the risk factors that can contribute to injury in athletes (4).
Hence the importance of being present in all training programs in the various manifestations that can occur.
Eccentric contraction
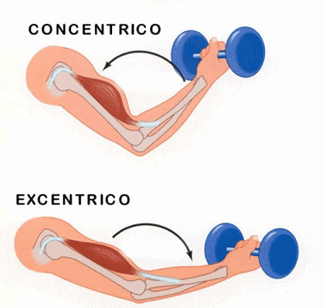
Normally when we speak of muscular contraction we refer to isometric, concentric and eccentric contraction (Figure 1).
Verhoshansky & Siff (8) describe eccentric contractions as those muscular actions in which the muscular force yields to a load and the muscular complex lengthens. Therefore, we understand it as that muscular work in which while the contraction exists, the muscle is stretching, so that the force contrary to the contraction is the one that will win.
.
Characteristics of eccentric work.
First, it should be noted that eccentric contractions are capable of generating higher forces and being metabolically more efficient compared to concentric contractions (8, 6). That is, they require less energy per unit of work (2).
It should be noted that as the speed of contraction increases, the maximum eccentric force also increases, and the maximum concentric force decreases (8).
In a systematic review by (6), they concluded that eccentric training seems to be more effective in obtaining greater muscle gains compared to concentric training. Attributing this fact to the greater degree of force demanded during eccentric actions.
On the other hand, it is understood to be very useful in the prevention of muscular injuries (1). Taking into account that many muscle injuries occur in actions with high eccentric demand (7).
The eccentric regime tasks are also found within the exercises for the prevention of patellar tendinopathy in team sports (5).
Likewise, eccentric exercises at high speeds, applied progressively and with overloads can make the connective tissue, especially that of the muscle-tendon junction, resist high impact forces, such as running, jumping and other actions involving momentum (8).
This aspect is of vital importance in all collective sports in which the joint impact component is important (basketball, volleyball, soccer, handball, among others).
In conclusion, a publication in review format shows that eccentric training can provide improvements in muscular strength, speed, power, as well as in the shortening-stretching cycle (2).
The Muscle Tightener
Also known as Russian Belt or Spanish Squat, during the last few years it has awakened interest in the world of sports training due to its eccentric action. In addition to the media effect that has had its use for professional soccer teams among others.
Version AMATEUR (la + económica) del CR-TM (marca registrada) dirigido a todo tipo de DEPORTISTAS - SIN acolchado- Poliéster muy resistente
Fabricado en España
CINTURÓN RUSO (poliéster) + ALARGADOR (poliéster) + MOCHILA DE TRANSPORTE (de nylon)
One of its main characteristics is the low risk of injury it presents and the safety with which it allows to develop an improvement of the muscle-tendon system (3).
It should be noted that it is a training tool that is easy to transport and use in various sports scenarios.

.
Musculator brace study
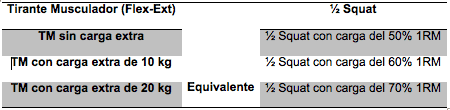
In the study by Edir et al, (3) a comparison was made between the half squat exercise and the extension flexion exercise with the brace musculator by performing surface electromyography and perception of effort.
The results obtained indicated that:
.
So it was concluded that the muscle pulldown was a good method to develop vastus quadriceps externalis muscle strength, using less external load.
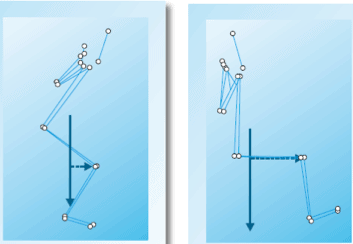
The center of gravity and the line of force application.
It was observed how the distance between the line of force application, body weight in the brace, and body weight plus overload in half squat, and the axis of the knees were different (3).
In the muscle brace the distance of force application with respect to the knee was much greater, therefore, the moment of force for the same force is greater the greater its distance.
On the other hand, in the half squat, to achieve the same moment of force as in the brace, since the distance is shorter, the force must be increased by increasing the weight.
So it seems to be a good tool to use to avoid the use of excessively high external loads, especially in those subjects where there is a risk of injury to the spine, since it avoids overloading that area (3).
.
Final considerations eccentric training and muscle brace.
Having described the characteristics and benefits of eccentric contractions, we can conclude that they should be taken into account within our training programs, and more so in those team sports with high demands of decelerations and accelerations, without forgetting the other contraction regimes.
On the other hand, we believe that the muscle brace is a good tool to consider despite the few studies that have been found in this regard.
However, we believe that it should be included in training programs, due to its ease of use and among others in order to respond to the principle of variability in sports training.
Bibliographical references
- Casáis, L. (2008). Review of strategies for injury prevention in sport from physical activity. Apunts Medicina de l’Esport, 43(157), 30-40.
- Douglas, J., Pearson, S., Ross, A., Mcguigan, M., & Douglas, J. (2016). Chronic Adaptations to Eccentric Training : A Systematic Review. Sports Medicine.
- Douglas, J., Pearson, S., Ross, A., Mcguigan, M., & Douglas, J. (2017). Eccentric Exercise : Physiological Characteristics and Acute Responses. Sports Medicine, 47(4), 663-675.
- Edir, M., Silva, D., Padullés, J. M., Álvarez, V. N., Luis, J., & Alonso, L. (2005). Electromyographic and perceived exertion analysis of the brace musculator with respect to the half squat exercise. Apunts Physical Education and Sports, 82, 45-52.
- Parkkari, J., Kujala, U. M., & Kannus, P. (2001). Is it Possible to Prevent Sports Injuries ? Review of Controlled Clinical Trials and Recommendations for Future Work, 31(14), 985-995.
- Peña, J., Moreno-doutres, D., Borràs, X., Altarriba, A., Baiget, E., Caparrós, A., & Buscà, B. (2017). Patellar Tendinopathy in Team Sports : Preventive Exercises. Strenght and Conditioning Journal, 0.
- Roig, M., Brien, K. O., Kirk, G., Murray, R., Mckinnon, P., Shadgan, B., & Reid, W. D. (2009). The effects of eccentric versus concentric resistance training on muscle strength and mass in healthy adults : a systematic review with meta-analysis.Journal Sports Med, 43, 556-568.
- Thacker, S. B., Gilchrist, J., Stroup, D. F., & Kimsey, C. D. (2003). The Impact of Stretching on Sports Injury Risk : A Systematic Review of the Literature. American College of Sports Medicine, (1), 371-378.
- Verkhoshansky, Y., & Siff, M. C. (2004).Super training(2nd ed.). Barcelona:Paidotribo.
AUTHOR : ELOI SADURNÍ RÀFOLS. Student of Master in Sports Training, Physical Activity and Health. Faculty of Psychology, Education and Sport Sciences. Blanquerna-URL.


