In the following article, it is explained what teaching styles in Physical Education are, their characteristics, which are used in the classroom, and based on what some can be used or are more appropriate than others.
Similarly, it addresses the importance of the change that has been occurring in recent years, from a traditional perspective to an active perspective, where the center of teaching is the students.
What are teaching styles?
Before delving into teaching styles in physical education, we must know a broader term, the models, defined as the set of procedures, resources, and techniques that teachers use to organize the activities carried out for the students.
The teaching styles in Physical Education are the climate generated to impart or teach students, the way of generating stimulation and organization used to teach and generate interactions between the student and the teacher.
In short, these help to understand and know or answer the questions: what is teaching and what is learning.
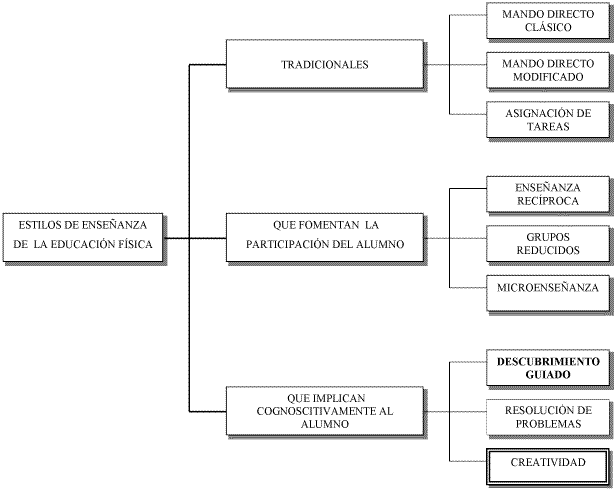
Two types of teaching styles in Physical Education stand out: one that refers to or follows a traditional pattern, and another that presents the student as the center and involves them cognitively to improve their learning (active).
Physical Education presents the possibility of covering large and different paths in relation to the methodology used, allowing the student to have to follow a series of guidelines directly guided by the teacher, or an involvement, participation, and work of the students through a more active process (1).
What are the teaching styles according to Muska Moston?
Muska Mosston and Sara Ashworth, in 1982, define what a teaching style is:
It is an attempt to convey everything that must be taken into account when preparing and conducting a session, and it is part of a specific way of acting by the teacher in the teaching-learning (T/L) process.
What are the teaching styles in Physical Education?
There are many classifications of teaching styles in Physical Education.
Focusing on one of them, two large groups are distinguished; on one hand, styles with less decision-making power by the student (traditional) and on the other, those that give greater responsibility, autonomy, and participation to the student (cognitive, participatory, socializing, and creative) (3).
The group of participatory styles includes the following:
- reciprocal teaching: usually done in pairs, one of the two performs the exercise and the other observes and evaluates it, then they switch roles.
- small groups: similar to the previous one, but the roles are distributed among the different members of the groups, which consist of 3-4 participants.
- microteaching: the student assumes the role of teacher during an activity.
In these, the student manages the teaching process and becomes an active part of the construction of knowledge (3).
Traditional models:
- direct command: the teacher makes the decisions and the student is limited to executing the orders received.
- task assignment: the teacher proposes tasks and the student executes them based on the role they have been assigned.
What is task assignment in Physical Education?
Although active styles are the styles that most favor critical thinking, reflection… overall, the integral development of the student, teachers use the traditional teaching style more, with the last style used being the creative styles, where student autonomy is very high, and the teacher has a guiding role (2).
Characteristics of teaching styles
- TRADITIONAL STYLES:
- automation of gestures
- fast learning
- specific solution
- PARTICIPATORY STYLES: (4)
- cooperative learning
- improvement of external regulation
- promotion of relationships with others
- improvement of self-esteem
- increase in responsibility and motivation capacity.
- try not to spend excessive time on verbalization, and encourage the search for solutions that involve movement (5)
- it is essential to always respect the student’s level of development and give autonomy progressively based on this.
Knowing the characteristics of both groups, the ideal is to hybridize them, and depending on the characteristics of the group, age, maturity, session, sport, etc., use one or the other according to the moment.
Classification of teaching styles in physical education
Below are two classifications of teaching styles in physical education, based on the technique and strategy used (6):
According to the teaching technique
-
Direct instruction or model reproduction: The teacher provides the students with direct information about the solution to a problem. Once the student knows how to execute the action based on the details, they execute it and through feedback, they correct and execute the action again, seeking in each repetition to minimize the error, until improving the result and automating the gesture.
-
Inquiry or search: Significantly increases the importance of the learning process. It focuses on the student. The teacher’s role is to motivate the student and guide their search towards appropriate solutions to the problems, with the correct answer not being just one, but with many possible solutions existing.
Based on the practice strategy
- Traditional:
-
Pure analytical: The task is divided into several parts, practicing all the components in isolation and synthesizing them all once they have been internalized, the order is established by the teacher according to the proposed objectives.
-
Sequential analytical: It is divided into parts and execution begins with the first part, once controlled and treated, it moves to the second, then the third, and so on until the last. When all the actions are internalized, they are combined.
-
Progressive analytical: starts with a single element and once mastered, new elements are progressively added. E.g.: part A, part A + B, part A + B + C.
-
- Active:
-
Pure global: Execution of the task in its entirety, starting from the real situation.
-
Global focusing attention: Real situation, but focusing attention on a specific or important point of execution.
-
Global modifying the real situation: The conditions for executing the task are modified. These can be changed to increase the difficulty of execution or, on the contrary, to generate simpler variants that favor control and learning.
-
-
Mixed: Combines the previous strategies.
Examples of teaching styles in physical education
To facilitate understanding, several examples of teaching styles of the possibilities that exist in different disciplines or content that can be addressed within the area of Physical Education are shown:
- EXAMPLES OF TRADITIONAL TEACHING STYLES:
- Aquagym
- Zumba
- Bodycombat
- Ballroom dancing
- At the level of technical executions:
- In handball: high pass tasks, where the body position and ball grip are explained
- In badminton: serve exercise, where the teacher details the grip of the racket, the body position, and the area of the court where the shuttlecock should be sent.
- EXAMPLES OF STYLES THAT FAVOR PARTICIPATION:
- Discovery of volleyball tactical actions from images of the court with different player placements, where they have to play and see what happens and how the opposing team responds.
- Treatment of different passes in basketball: students have a sheet with different options, and they try to see the characteristics of each one and the existing advantages or difficulties, then they explain it to the other groups.
Conclusion
As we can see, there are different teaching styles in physical education. Each and every one of them is valid for certain moments and contexts.
There is no universally valid method. In this sense, the teacher must apply the teaching method that best suits the characteristics of the students, their environment, and the objectives to be achieved.
The fundamental idea that is intended to be conveyed is the importance of the teacher’s knowledge of this series of resources to use them correctly and achieve great performance and efficiency in the teaching-learning process.
The objective of this article is for you to know all the teaching styles in Physical Education and to apply the most appropriate one according to the situation in question.
Bibliographic references
- Ayuso, J. A. Z. (2018). BENEFITS OF TEACHING STYLES AND STUDENT-CENTERED METHODOLOGIES IN PHYSICAL EDUCATION [Benefits of teaching styles and student-centred methodologies in Physical Education]. E-balonmano. com: Revista de Ciencias del Deporte, 13(3), 237-250.
- Mateos, M. E., & Pineño, P. J. (2020). Identification of the preferred teaching styles by Physical Education teachers in Secondary Education. Revista de Estilos de Aprendizaje, 13(25), 167-182.
- Delgado-Noguera, M.A. (1991). Teaching styles in Physical Education: proposal for a teaching reform. Granada: University of Granada
- Rando, C. (2010). Teaching styles in Physical Education. Use according to the analysis of learning tasks and the characteristics of students. Physical education and sport. Digital magazine.(146). Retrieved from www. efdeportes. com/efd146/estilosde-ensenanza-en-educacion-fisica. htm.
- Lebrero-Casanova, I., Almagro, B. J., & Sáenz-López, P. (2019). Participatory teaching styles in Physical Education classes and their influence on different psychological aspects.
- Nieto, B. H. (2009). Teaching methods in Physical Education.