Ruffier Test (Cardiovascular Health Test)
| Índice de Ruffier | Fitness level |
|---|---|
| 0 – 0,1 | Excelent |
| 0,2 – 5 | Very good |
| 5,1 – 10 | Average |
| 10,1 – 15 | Low |
| >15,1 | Very low |
With this tool, you can calculate cardiac recovery capacity and aerobic endurance. This calculator for the Ruffier test will give you an idea of your current physical condition. The most efficient way to perform it is with a heart rate monitor, although you can get an idea by taking your pulse at the carotid artery (next to the Adam’s apple) or at the radial artery (on the wrist).
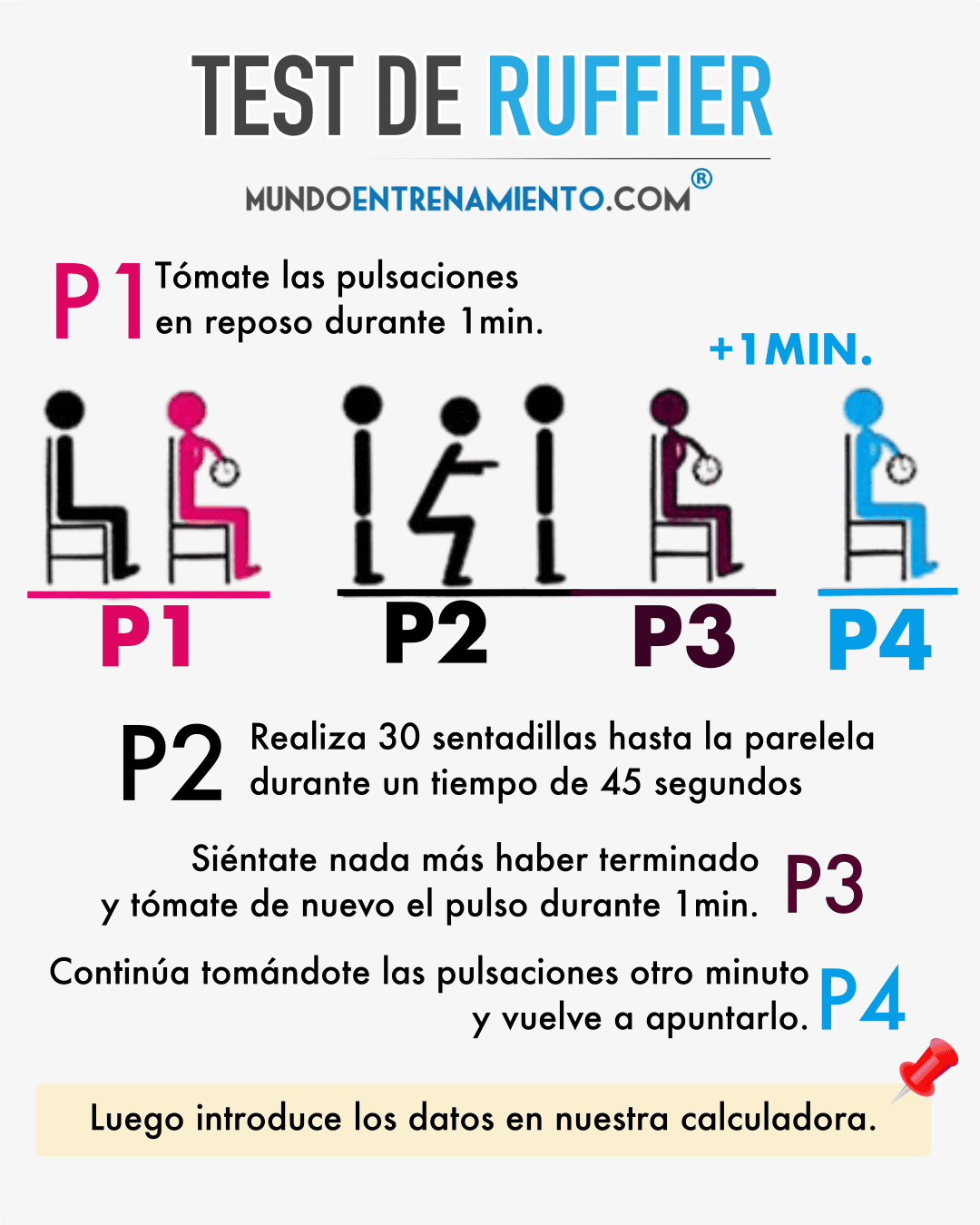
How is the Ruffier test performed?
- Sit in a chair and take your resting pulse at the carotid artery in the neck (P1).
- Then stand up, set a timer, and perform 30 consecutive squats to parallel with the ground, for a duration of 45 seconds. If you are unable to do them within that time, try to do at least 30 repetitions (as long as you do not exceed one minute) (P2).
- Sit down again and take another pulse reading and record it (P3).
- Continue taking your pulse for another minute and record it again (P4).
- Enter the data into our Ruffier test calculator.
Frequently asked questions
What is the Ruffier test?
The Ruffier test is a simple test that evaluates cardiovascular condition and the heart’s recovery capacity after mild physical exertion.
How is the Ruffier test performed?
The test is performed by measuring the resting heart rate, after doing 30 squats in 45 seconds, and again one minute after the exercise.
What is the purpose of the Ruffier test?
[article ids=”98471″] It is used to evaluate the heart’s ability to recover after exertion, providing an indication of a person’s physical and cardiovascular condition.
What does the Ruffier index measure?
The Ruffier index measures the efficiency of the cardiovascular system and is calculated using heart rates measured before, during, and after exertion.
How is the Ruffier index calculated?
The index is calculated with the formula: (P1 + P2 + P3 – 200) / 10, where P1 is the resting heart rate, P2 after the squats, and P3 after one minute of rest.
What do the results of the Ruffier test mean?
A low index indicates good cardiovascular condition, while a high index may indicate low recovery capacity and less optimal physical condition.
Is the Ruffier test suitable for everyone?
It is not suitable for people with cardiovascular problems, hypertension, or injuries that prevent them from doing squats. It is advisable to consult a doctor before performing it.
How often should the Ruffier test be performed?
The test can be performed every few months to assess changes in cardiovascular condition, especially when following physical training programs.
